pylist
Check If a String Is a Valid Sequence from Root to Leaves Path in a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree where each path going from the root to any leaf form a valid sequence, check if a given string is a valid sequence in such binary tree.
We get the given string from the concatenation of an array of integers arr and the concatenation of all values of the nodes along a path results in a sequence in the given binary tree.
Example 1:
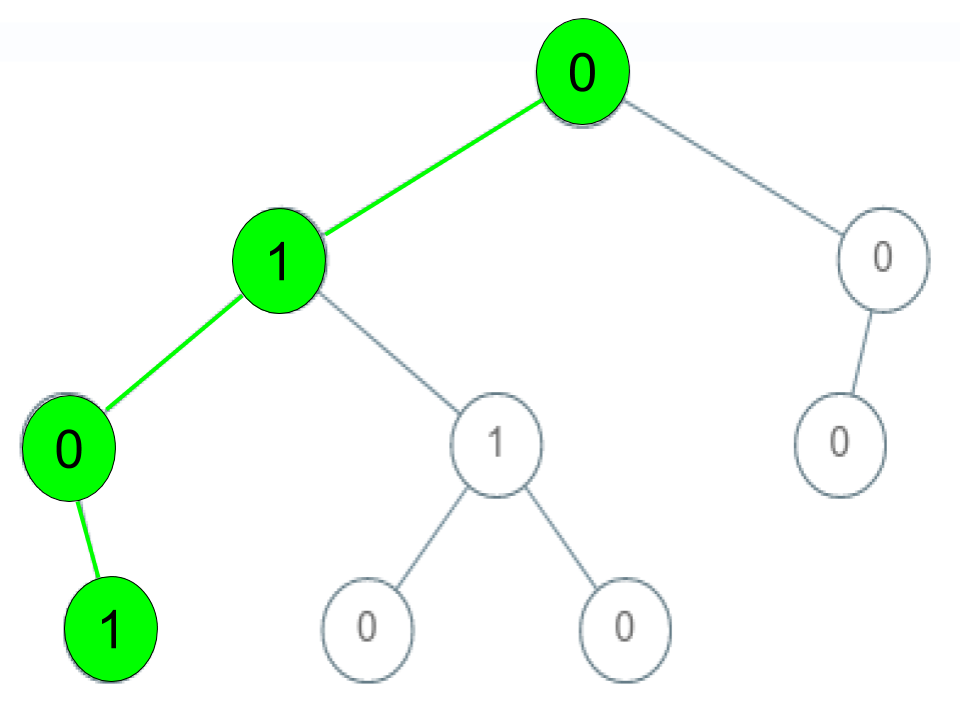
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,0,1]
Output: true
Explanation:
The path 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 is a valid sequence (green color in the figure).
Other valid sequences are:
0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0
0 -> 0 -> 0 Example 2:
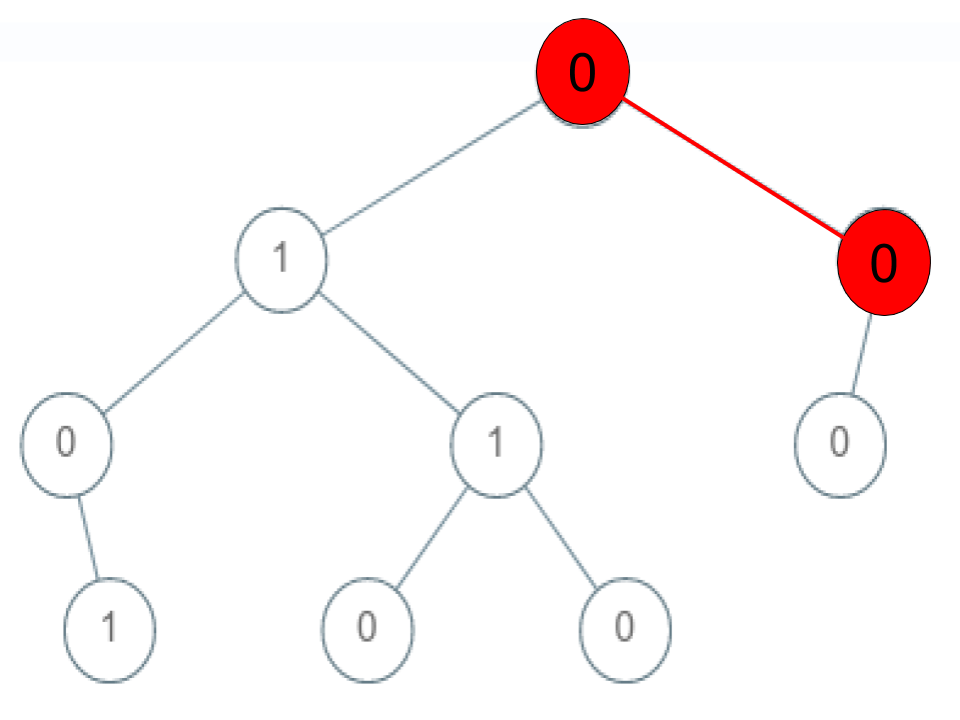
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,0,1]
Output: false
Explanation: The path 0 -> 0 -> 1 does not exist, therefore it is not even a sequence. Example 3:
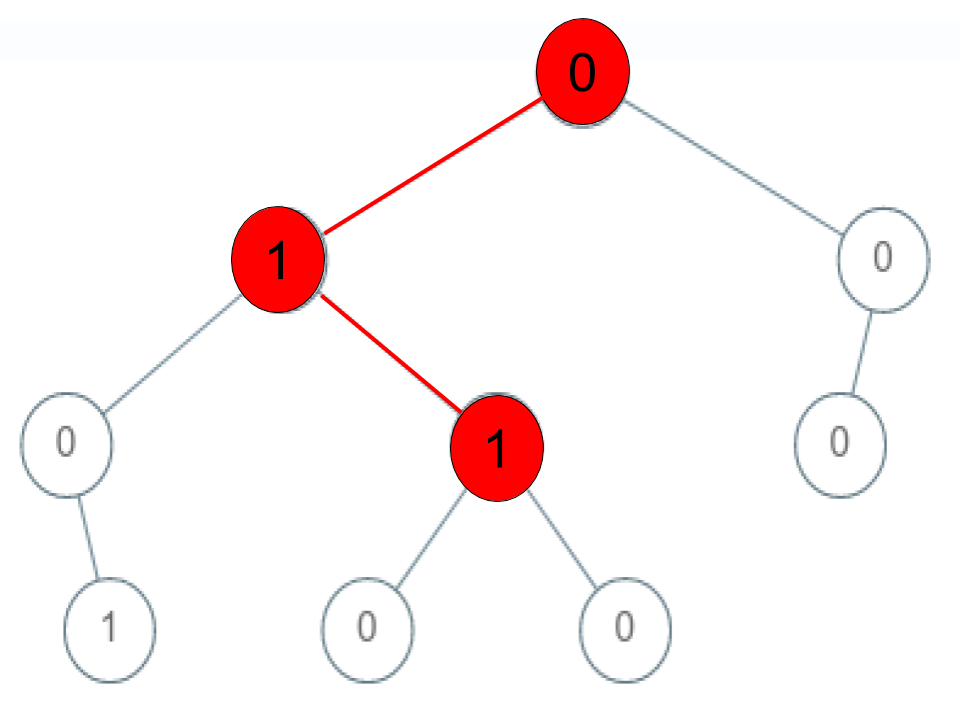
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,1]
Output: false
Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 1 is a sequence, but it is not a valid sequence.
Constraints:
- 1 <= arr.length <= 5000
- 0 <= arr[i] <= 9
- Each node’s value is between [0 - 9].
Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidSequence(self, root: TreeNode, arr: List[int]) -> bool:
# read only data
self.arr = arr
# dummy root
dummy = TreeNode()
dummy.left = root
cur = []
found = [False]
# start the recursion
self.traverse(dummy, cur, found)
return found[0]
def traverse(self, node, cur, found):
# if found
if found[0]:
return
# return condition
# if cur is long enough
if len(cur) == len(self.arr):
# if not leaf
if node.left is not None or node.right is not None:
return
# cur is a valid sequence with same legth as arr:
# if the same
if cur == self.arr:
found[0] = True
return
else:
return
# cur is not long enough :
# recursion logic
if node.left is not None:
self.traverse(node.left, cur + [node.left.val], found)
if node.right is not None:
self.traverse(node.right, cur + [node.right.val], found)
return
Care
- 二叉树的travers 需要 dummy root
- 递归之前需要判断左右节点的存在性
- 这样就不像 DC 那样有两个 和 None 有关的返回条件了
- 事实上一个都没有,全部的逻辑都在 return condition 部分
- 这样就不像 DC 那样有两个 和 None 有关的返回条件了