pylist
297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
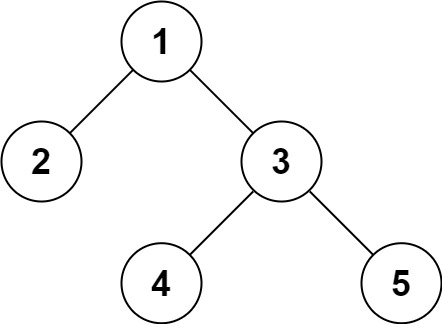
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 4:
Input: root = [1,2]
Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 10000].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
"""Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
# corner case
if root is None:
return ""
# regular case
out = [str(root.val)] # append value when enqueue
q = deque([root]) # put root in queue
while q: # while queue not empty
# pop
node = q.popleft()
# children
for attr in ['left', 'right']:
if getattr(node, attr) is None:
# corner case
out.append('*')
else:
# regular case
## Process the child
out.append(str(getattr(node, attr).val)) # append value when enqueue
## append the child
q.append(getattr(node, attr))
return ','.join(out) # list to string
def deserialize(self, data):
"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# corner case
if data == "":
return None
# regular case
data = data.split(',') # string to list
root = TreeNode(int(data[0])) # create node when enqueue
q = deque([root]) # put root in queue
i = 1 # index of data
while q: # while queue not empty
# pop
node = q.popleft()
# children
for attr in ['left', 'right']:
# corner case dealt with default value
if data[i] != '*':
# regular case
## Process
setattr(node, attr, TreeNode(int(data[i]))) # create node when enqueue
## append the child
q.append(getattr(node, attr))
i += 1 # move data index forward
return root # return root
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# ser = Codec()
# deser = Codec()
# ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root))
思路
- 这个答案有别于模板的地方是,
模板中,node 的处理是在 出队列 的时候完成的。
而这一题中,对 node 的处理是在 入队列 的时候完成的。
其原因是,一般情况下,操作是在 树 本身上进行的,即不包括 为 None 的子树。
而这一题是在 增广树 上进行的, 即包括了 为 None 的子树。
以下代码并不能运行。
while q: node = q.popleft() node = TreeNode(int(data[i])) for attr in ['left', 'right']: q.append(getattr(node, attr)) -
- 因为在
node = TreeNode(int(data[i]))这一步,建立了新的变量node。 所以必须在 母节点 上对 子树 赋值, 而不能将子树 压入队列 之后再赋值。
- 因为在
- 这个答案优雅的地方在于,解码和编码的结构完全一样
python 细节
- decoder 里,之所以
data = [int(d) for d in data.split(',')]不行,是因为中间有*- 另外说,int 没有 inf 的值,只有 float 有
getattr和setattr不是成员函数,而是 built-in- decoder 也可以用 deque 就可以省去记录一个 index,如下
def deserialize(self, data): """Decodes your encoded data to tree. :type data: str :rtype: TreeNode """ if data == "": return None data = deque(data.split(',')) root = TreeNode(int(data.popleft())) q = deque([root]) while q: node = q.popleft() for attr in ['left', 'right']: val = data.popleft() if val != '*': setattr(node, attr, TreeNode(int(val))) q.append(getattr(node, attr)) return root1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,37,38,39,40,41,42,66,67,68,69 20 19 21 22 24 31 33 23 25 26,27 29,30 32 34 28 35 18 15,16 17 47 48 49 50 51 52 54 59 61 53 55 56 57,58 60 62 63 64 46 43,44 45