pylist
133. Clone Graph
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
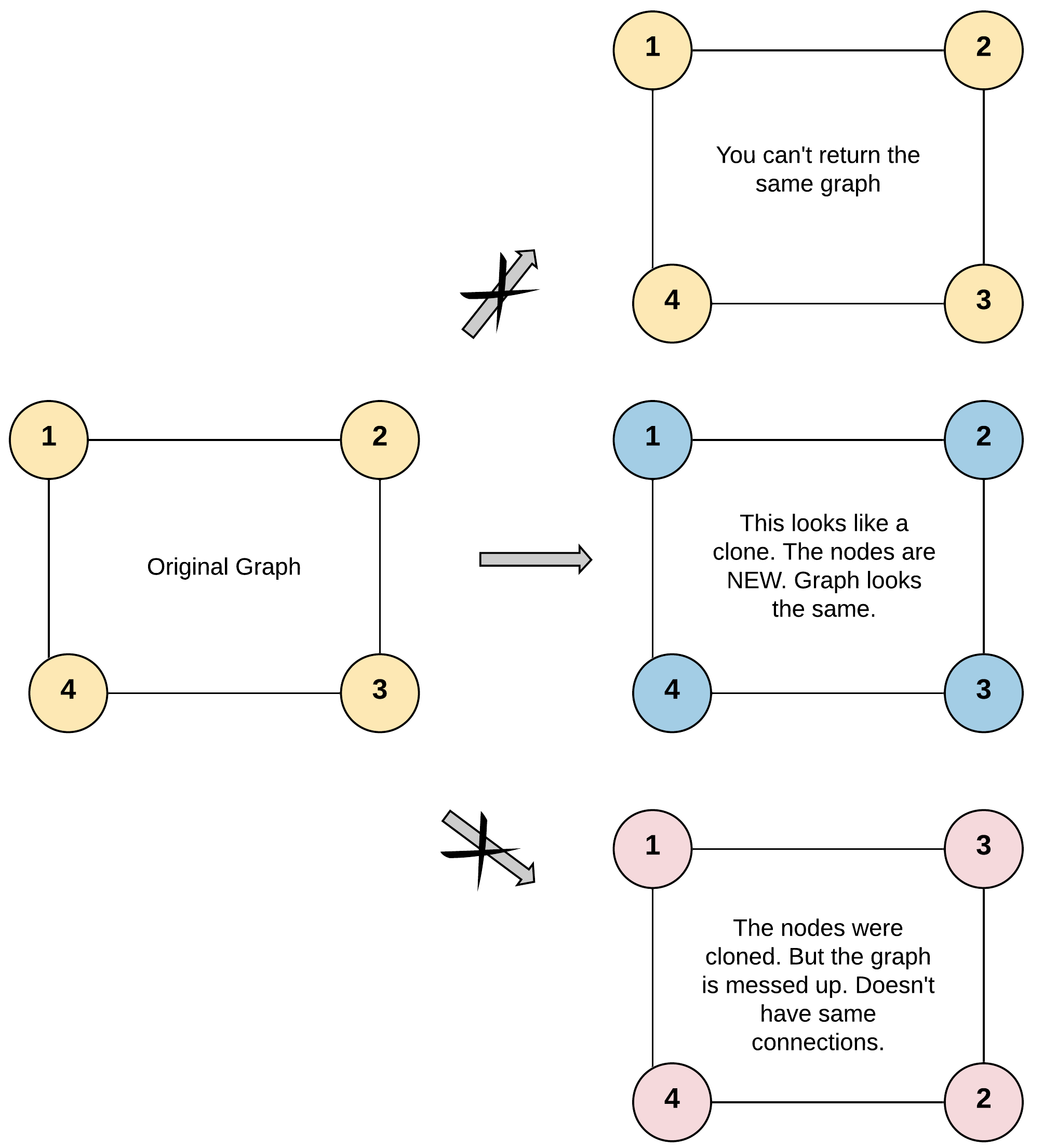
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
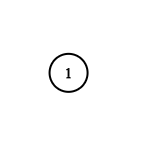
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = []
Output: []
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range [0, 100].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
- Node.val is unique for each node.
- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Solution
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0, neighbors = None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
"""
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
# corner case
if root is None:
return None
# clone nodes by BFS
old2new = dict() # key: old node, val: new node
q = deque([root])
qed = set(q)
while q:
# pop
old_node = q.popleft()
# Process
old2new[old_node] = Node(val=old_node.val)
# append children
for old_nei in old_node.neighbors:
if old_nei not in qed:
q.append(old_nei)
qed.add(old_nei)
# clone edge
for old_node in old2new:
for old_nei in old_node.neighbors:
old2new[old_node].neighbors.append(old2new[old_nei])
return old2new[root]
要点
- 因为是依照旧图造新图,所以 dict 里也是依照旧节点找新的节点
- 几乎所有构建图都是先节点再边
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 13 27 14 15 16 17 18 20 22 19 21 23 24 25 26 28 29 30 31 10 11,12
Advanced Solution
Use qed as record, no extra dixtionary
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0, neighbors = None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
"""
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
# corner case
if root is None:
return None
# clone nodes by BFS
q = deque([root])
qed = {root: Node(val=root.val)} # key: old node, val: new node
while q:
# pop
old_node = q.popleft()
# append children
for old_nei in old_node.neighbors:
if old_nei not in qed:
q.append(old_nei)
qed[old_nei] = Node(val=old_nei.val) # record enqueue and process
# clone edge
for old_node in qed:
for old_nei in old_node.neighbors:
qed[old_node].neighbors.append(qed[old_nei])
return qed[root]