pylist
1026. Maximum Difference Between Node and Ancestor
| Given the root of a binary tree, find the maximum value V for which there exist different nodes A and B where V = | A.val - B.val | and A is an ancestor of B. |
A node A is an ancestor of B if either: any child of A is equal to B, or any child of A is an ancestor of B.
Example 1:
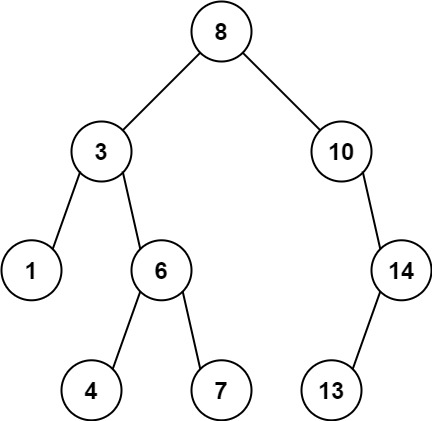
Input: root = [8,3,10,1,6,null,14,null,null,4,7,13]
Output: 7
Explanation: We have various ancestor-node differences, some of which are given below :
|8 - 3| = 5
|3 - 7| = 4
|8 - 1| = 7
|10 - 13| = 3
Among all possible differences, the maximum value of 7 is obtained by |8 - 1| = 7.
Example 2:
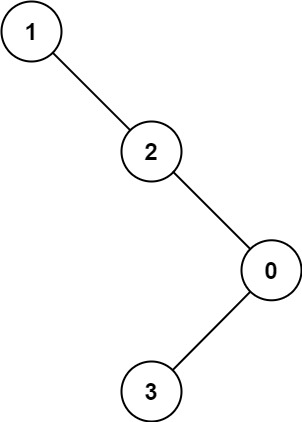
Input: root = [1,null,2,null,0,3]
Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 5000].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 105
Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxAncestorDiff(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
self.V = 0
self.dfs(root)
return self.V
def dfs(self, node):
if node is None:
return 0, float('inf')
if node.left is None and node.right is None:
return node.val, node.val
lmax, lmin = self.dfs(node.left)
rmax, rmin = self.dfs(node.right)
self.V= max([self.V,
node.val - lmin,
node.val -rmin,
lmax - node.val,
rmax -node.val])
treemax = node.val
treemin = node.val
treemax = max([treemax, lmax, rmax])
treemin = min([treemin, lmin, rmin])
return treemax, treemin
Details:
self.Vis a global variable. The solution is a mix of DC and traverse- There is no need to add
abs()innode.val - lmin, becauselmax - node.val>=lmin - node.valis guaranteed.